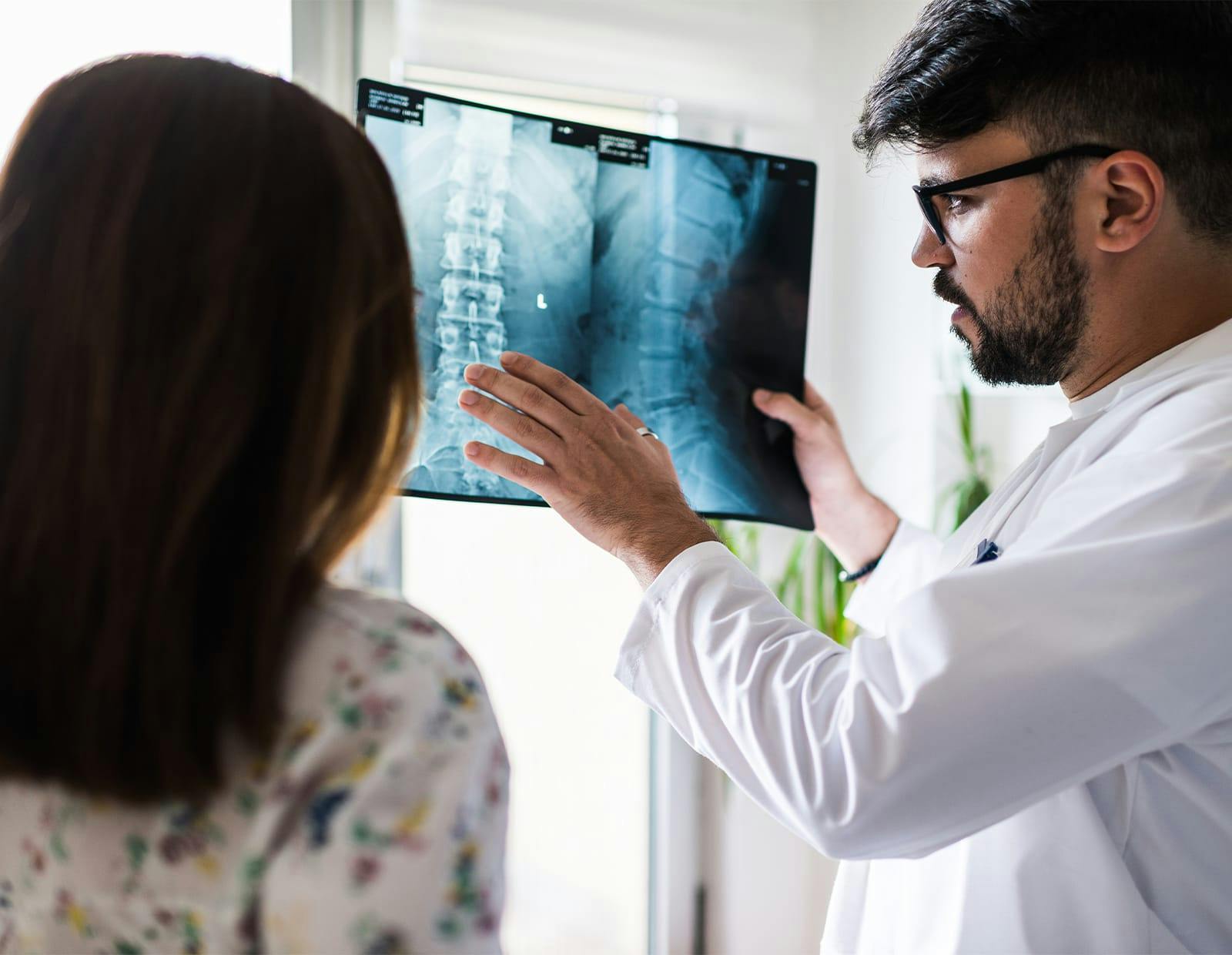
Spinal fractures are serious injuries that involve a break or crack in the vertebrae, the bones that make up the spine. These fractures can result from trauma, such as car accidents or falls, or from medical conditions like osteoporosis. The severity of spinal fractures can vary widely, from mild fractures that cause minimal pain to more severe cases that affect the spinal cord, leading to significant nerve damage and potential paralysis. Treating spinal fractures promptly is critical to prevent further complications and ensure the best possible recovery.
Symptoms of Spinal Fractures
The symptoms of spinal fractures can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and neurological damage, depending on the location and severity of the fracture. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Sudden, severe back or neck pain is often the most noticeable symptom. The pain may worsen with movement or pressure on the spine.
- Numbness or tingling: If the fracture compresses or damages the spinal nerves, patients may experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms, legs, or other areas.
- Loss of mobility: Severe fractures can cause loss of mobility, making it difficult to move the back or neck.
- Paralysis: In cases where the spinal cord is damaged, paralysis below the injury site can occur.